What is Benchmarking?
Benchmarking is a systematic process of measuring your organization’s performance, processes, and practices against those of top-performing companies. It enables businesses to identify gaps, adopt best practices, and set clear improvement goals. Far beyond just comparing numbers, benchmarking drives strategic decisions that enhance efficiency and competitive positioning.
Benchmarking in Business Context
In business, benchmarking is used to evaluate key functions and metrics across your organization against your competitors and industry leaders. This helps companies understand market standing and uncover opportunities to innovate or improve operations.
Types of Benchmarking
- Internal Benchmarking: Comparing performance across departments or teams within the same organization.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Analyzing competitors directly in the same industry or market segment.
- Functional Benchmarking: Studying processes and functions similar to yours but in different industries.
- Generic Benchmarking: Assessing universal best practices applicable across any sector, regardless of industry.
Why Benchmarking is Crucial for Your Business
- Identifies performance gaps and areas that require improvement.
- Promotes a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
- Keeps your business aligned with industry trends and best practices.
- Improves customer satisfaction by boosting service quality and delivery.
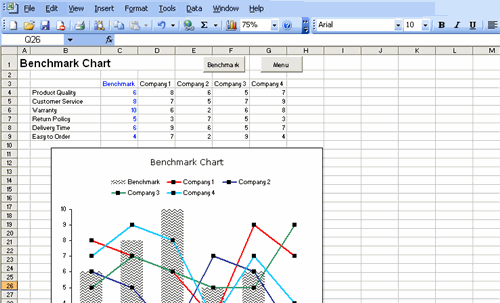
Benchmarking enables businesses to set clear, targeted goals by learning from the best practices of market leaders. By adopting these practices and adjusting strategies accordingly, companies can increase efficiency, productivity, and overall business success.
The 7 Essential Steps of Effective Benchmarking
- Preparation and Planning
Define the scope, objectives, and key areas to benchmark. Develop a clear methodology, allocate resources, and establish timelines. - Data Collection
Gather accurate, relevant data from both internal sources and external benchmarks using surveys, reports, industry studies, and competitive analysis. - Data Analysis
Analyze the collected data to identify patterns, performance gaps, and root causes. Use statistical tools and comparative techniques. - Reporting
Prepare concise, actionable reports that clearly communicate findings to stakeholders using visual aids such as charts and dashboards. - Learning from Best Practices
Research and understand top-performing companies’ strategies and processes. Identify which practices are transferable to your organization. - Implement Improvement Measures
Develop a detailed action plan to close performance gaps. Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and track progress. - Institutionalizing Learning
Embed new practices and insights into your company culture. Update policies, training, and continuous monitoring systems to sustain improvements.
Real-World Benchmarking Examples
- Business Process Benchmarking: Comparing operational workflows with leading organizations to increase speed and quality.
- Product Benchmarking: Assessing product features, quality, and pricing against market leaders.
- Performance Benchmarking: Evaluating financial, productivity, or customer service metrics against high-performing companies.
Niche Examples by Industry
- Manufacturing: Benchmarking supply chain efficiency and defect rates against industry leaders to reduce costs and improve quality.
- Retail: Comparing customer retention strategies and loyalty program effectiveness with top retailers.
- Technology: Analyzing product development cycles and innovation rates to speed up time-to-market.
How to Streamline Your Benchmarking Process
Successful benchmarking can be integrated through a straightforward, scalable approach.
Step 1: Identify Key Best Practices
Focus on crucial business drivers such as sales, operations, financial health, HR, and customer satisfaction. Look beyond your industry for innovative ideas.
Step 2: Efficient Data Collection System
Set up reliable data pipelines from industry reports, public records, surveys, and analytics platforms. Consider subscription services for niche metrics.
Step 3: Define Clear Metrics and KPIs
Select measurable KPIs that reflect critical success factors. Examples include customer churn rate, production downtime, or average sales per employee.
Step 4: Develop Continuous Reporting Cycles
Implement regular, digestible reporting formats. Use dashboards for real-time insights and decision-making support.
Benchmarking Challenges and Tips
- Benchmarking requires initial investment in time and resources—plan accordingly.
- Ensure data accuracy and relevance to avoid misleading conclusions.
- Always adapt best practices to your unique business context, do not blindly copy.
- Engage cross-functional teams throughout to enhance buy-in and knowledge sharing.
Benchmarking Action Plan: A Workbook Guide
| Step | Action Item | Responsible Person | Deadline | Notes/Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define benchmarking objectives and scope | Strategy Lead | MM/DD/YYYY | Focus on customer satisfaction metrics |
| 2 | Identify data sources & collect baseline data | Business Analyst | MM/DD/YYYY | Use industry reports and past internal data |
| 3 | Analyze data to find performance gaps | Data Scientist | MM/DD/YYYY | Highlight top 3 improvement areas |
| 4 | Develop improvement action plan | Operations Manager | MM/DD/YYYY | Initiate pilot project for customer service |
| 5 | Implement changes and monitor progress | Team Leads | MM/DD/YYYY | Weekly progress reporting required |
| 6 | Institutionalize effective practices | HR & Training | MM/DD/YYYY | Update training manuals and SOPs |
This structured approach can help maintain focus and accountability during your benchmarking journey.
Additional Resources to Enhance Benchmarking
- Boost your operational insights with the Financial Dashboard Excel Template.
- Streamline your reporting and performance tracking using the Automated Excel Reporting tool.
- Explore strategies to optimize pricing and profitability with the 101 Ways to Optimize Pricing & Profit guide.
Conclusion
Benchmarking is a powerful strategic tool that, when executed with discipline, uncovers valuable insights to elevate your business performance. By consistently measuring your results against industry leaders and embedding learned improvements, you develop a resilient, high-performing organization ready to excel in today’s competitive market.
Take the next step in your benchmarking journey by leveraging tailored resources that automate and simplify data tracking, reporting, and performance analysis.






























