Understanding Business Metrics and KPIs
Every day, organizations and business professionals rely on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), ratios, and business metrics—whether formally tracked or informally analyzed—to drive decisions and improve performance. Metrics such as profit margins, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), operating costs, customer retention rates, customer satisfaction scores, number of late orders, and volume of customer complaints serve as foundational measures helping businesses evaluate their operational health.
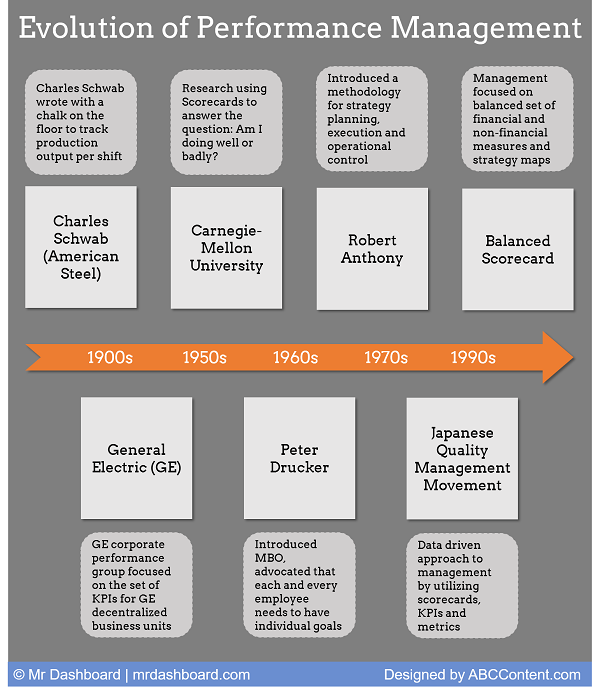
However, defining the most impactful metrics is essential when designing an organized performance management system. Selecting the right KPIs can feel overwhelming but is equally as critical as crafting a strategic business plan.
Why Are Business Metrics Important?
The well-known principle “what gets measured, gets improved” stands truer than ever in today’s competitive landscape.
- KPIs clearly reflect an organization’s strategic direction and operational priorities.
- Tracking the right metrics focuses the team on the most essential activities to achieve business goals.
- Tracking and reporting relevant KPIs fosters accountability, transparency, and continuous improvement.
To maximize their impact, KPIs must closely align with your organization’s strategy and core objectives.
Common Categories of Business Metrics and KPIs
Business metrics can be grouped into several broad categories. Below are key KPI categories with sample metrics organizations use to evaluate performance:
Financial Metrics
- Profit Margin
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Operating Expenses
- Return on Investment (ROI)
- Cash Flow
- Revenue Growth Rate
Customer Metrics
- Customer Retention Rate
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Number of Customer Complaints
Operational Metrics
- Number of Late Orders
- Order Fulfillment Time
- Inventory Turnover
- Supply Chain Efficiency
- Equipment Downtime
Employee and Productivity Metrics
- Employee Turnover Rate
- Absenteeism Rate
- Average Employee Productivity
- Training Hours per Employee
- Time to Hire
Industry-Specific KPI Examples
Different industries require unique KPIs tailored to their operational nuances and marketplace demands:
Retail
- Sales per Square Foot
- Average Transaction Value
- Customer Footfall
- Stock Shrinkage Rate
Manufacturing
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
- Production Yield Percentage
- Defect Rates
- Cycle Time
Service Industry
- First Response Time
- Chargeable Utilization Rate
- Client Satisfaction
- Project Margin
Healthcare
- Patient Wait Time
- Readmission Rate
- Patient Satisfaction Scores
- Average Length of Stay
How to Choose the Right KPIs for Your Business
To develop an effective set of KPIs that drive real business results, follow these steps:
- Align KPIs with Business Objectives: Ensure each metric supports a key goal or priority.
- Be Specific and Measurable: Only track KPIs that can be accurately measured and reported.
- Limit the Number of KPIs: Focus on quality over quantity to prevent data overload.
- Define Clear Targets: Assign benchmarks or goals to each KPI for performance evaluation.
- Regularly Review and Update: KPIs should evolve with your business strategy and market changes.
Sample KPI Selection Checklist
| Criteria | Yes / No | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Is the metric aligned to strategic objectives? | ||
| Is data for the metric readily available and reliable? | ||
| Can the metric be measured frequently and consistently? | ||
| Is the metric easy to understand by stakeholders? | ||
| Will the metric influence better decision-making? | ||
| Is the number of metrics manageable and focused? |
Next Steps: Organizing and Reporting KPIs Effectively
After identifying your key business metrics, organizing them into clear, visual dashboards or scorecards is crucial. This visualization helps decision makers monitor performance at a glance.
If you seek tools to automate your financial and business reporting efforts, explore the Automated Excel Reporting template to streamline KPI tracking and enhance data visualization.
Additionally, the Financial Dashboard Excel is a powerful resource to manage and analyze your financial KPIs with practical, ready-made tools that improve accuracy and save time.
Summary and Action Plan
To recap, effective business metrics and KPIs are foundational to driving success. Use the following quick action guide to start aligning your measures with your business strategy:
- Step 1: Define your top business goals.
- Step 2: Identify potential KPIs relevant to each goal.
- Step 3: Use the KPI selection checklist to narrow your list.
- Step 4: Set measurable targets for each KPI.
- Step 5: Implement reporting tools and visualize progress regularly.
- Step 6: Review and update KPIs quarterly to stay aligned with changing priorities.
By following these guidelines and continuously refining your KPIs, you will maintain a clear view of your organization’s health and enable faster, smarter decisions.
For a comprehensive solution to growing your business and financial success, consider exploring the Finance Profit & Growth Toolkit. It offers practical strategies and templates to boost your profitability and scalable growth.






























